What is Skin Pigmentation?
Skin pigmentation refers to the coloring or tone of the skin, which is primarily determined by a pigment called melanin. Melanin is produced by specialized cells in the skin called melanocytes. The level and type of melanin produced determine the skin’s color, ranging from fair to dark tones. However, certain conditions, genetic factors, and environmental influences can cause variations or irregularities in melanin production, leading to uneven skin pigmentation. This often manifests as darker or lighter spots on the skin, commonly known as pigmentation disorders.
What is pigment in skin?
Skin pigmentation plays an important role in protecting the skin from ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which can damage the skin’s cells. People with darker skin tones generally have higher melanin levels, offering more protection from the sun. Conversely, those with lighter skin tones have less melanin, making them more susceptible to sun damage and conditions such as sunburn or skin cancer.
Pigmentation of the skin
While pigmentation itself is a natural and essential component of skin health, when it becomes uneven or overly concentrated, it may lead to unwanted cosmetic concerns. These concerns are often referred to as pigmentation disorders or hyperpigmentation, and they are some of the most common reasons people seek pigmentation treatment.
Types of Skin Pigmentation

Skin pigmentation issues can appear in various forms, and understanding the different types is crucial for choosing the right pigmentation treatment. The most common forms of pigmentation include:
1. Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation occurs when there is an overproduction of melanin in certain areas of the skin, leading to darker spots. It can result from several factors such as sun exposure, hormonal changes, inflammation, or injury. The most common types of hyperpigmentation include:
- Sunspots (Solar Lentigines): Often caused by prolonged sun exposure, sunspots are flat, dark spots that appear on areas like the face, hands, and arms.
- Melasma: This is a common pigmentation issue, particularly among women. It typically occurs during pregnancy or due to hormonal changes from birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy (HRT). It results in large, brownish patches often found on the face.
- Post-inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): This type of pigmentation occurs after an injury or skin condition such as acne. It manifests as dark spots left behind after the skin heals.
2. Hypopigmentation
Hypopigmentation is the opposite of hyperpigmentation and occurs when there is a loss of melanin in certain areas of the skin. This leads to lighter patches of skin. Conditions such as vitiligo, albinism, or post-inflammatory hypopigmentation are some common causes of reduced melanin production. Vitiligo, for example, leads to white patches on the skin where melanocytes are no longer producing melanin.
3.Freckles
Freckles are small, flat, brownish spots that usually appear on areas of the skin exposed to the sun, such as the face and arms. They are typically hereditary and more common in individuals with fair skin tones. While they are not harmful, many people choose pigmentation treatments to lighten or eliminate them.
What is the main cause of skin pigmentation?
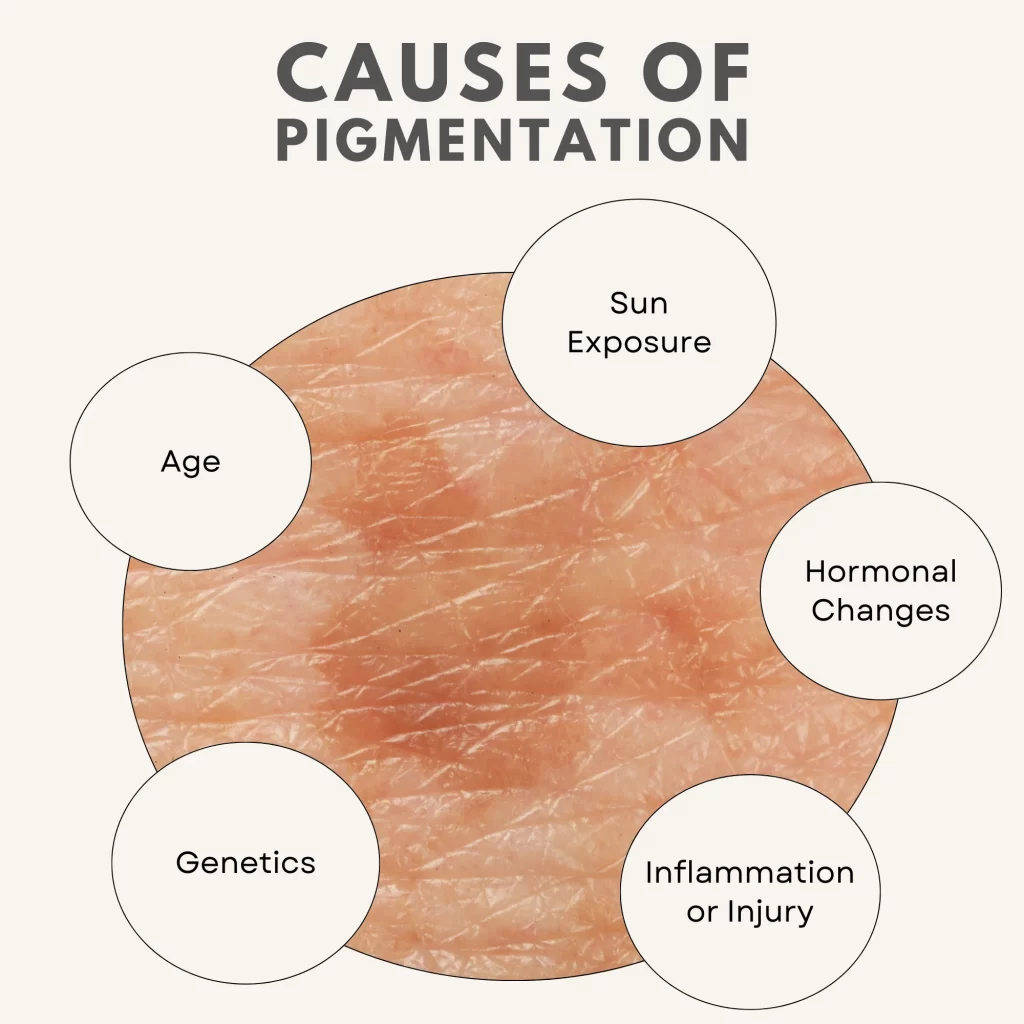
The main cause of skin pigmentation is the production of melanin, a natural pigment responsible for the color of the skin, hair, and eyes. Melanin is produced by cells called melanocytes, which are located in the epidermis (the outermost layer of the skin). The amount and type of melanin produced by melanocytes determine the skin’s color, ranging from light to dark shades.
However, several factors can influence melanin production, leading to variations in skin pigmentation. These include:
- Sun Exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun stimulate melanocytes to produce more melanin as a protective response to UV damage. This is why skin tans or darkens after prolonged sun exposure. Excessive sun exposure can also lead to pigmentation issues such as sunspots, age spots, and other forms of hyperpigmentation.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, especially during pregnancy, the use of birth control pills, or hormone replacement therapy (HRT), can trigger increased melanin production. This often leads to conditions like melasma, which causes dark patches, typically on the face.
- Inflammation or Injury: When the skin experiences trauma, such as cuts, burns, or acne, the healing process can result in post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), where dark spots are left behind after the injury heals.
- Genetics: Your genetic makeup plays a significant role in determining how your skin reacts to environmental factors like sun exposure. Some individuals are naturally more prone to developing pigmentation irregularities due to their genetic predisposition.
- Age: As we age, the skin’s ability to repair itself diminishes, leading to the development of age spots or liver spots (solar lentigines), which are caused by long-term sun exposure.
Skin Pigmentation Treatment
Skin pigmentation issues, such as dark spots, melasma, and uneven skin tone, can result from sun exposure, hormonal changes, or scarring. While these concerns are common, there are several effective treatments available to reduce pigmentation and restore even skin tone. Here are five popular skin pigmentation treatments:
Topical Creams and Serums
Topical treatments are commonly used to lighten dark spots and even skin tone. Ingredients like hydroquinone, vitamin C, and niacinamide are widely used to treat pigmentation. Hydroquinone inhibits melanin production, while Vitamin C brightens the skin and reduces sun damage. Niacinamide helps lighten dark spots and improve overall skin tone. These treatments are ideal for mild to moderate pigmentation issues.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels use a solution to exfoliate the skin, removing dead cells and stimulating fresh skin growth. This process helps fade dark spots, sun damage, and melasma. Chemical peels come in varying strengths, with superficial peels requiring minimal downtime and deeper peels offering more dramatic results for stubborn pigmentation.
Laser Treatments
Laser treatments, such as Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) or Fractional CO2 Lasers, are effective for treating deeper pigmentation issues like sunspots, melasma, and age spots. Lasers target and break down excess melanin, and the body gradually eliminates it. Multiple sessions may be required for optimal results.
Microneedling
Microneedling involves tiny needles that create micro-injuries in the skin, stimulating collagen production. This treatment helps reduce pigmentation from acne scars, sunspots, and uneven skin tone. Microneedling is often combined with serums to enhance the treatment’s effectiveness.
Sunscreen and Preventive Care
Prevention is key in managing skin pigmentation. Daily sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher helps protect against UV rays, preventing further pigmentation. Wearing protective clothing and avoiding peak sun hours can also minimize the risk of developing new pigmentation issues.
These treatments, combined with proper skincare, can help achieve a more even and radiant complexion.
FAQ
1 What is the main reason of face pigmentation?
Face pigmentation, or hyperpigmentation, can be caused by a number of factors, including sun exposure, hormonal changes, medications, and skin conditions.
2 How can I remove pigmentation from my face?
You can remove pigmentation from your face with topical treatments, chemical peels, laser treatments, and other procedures. You can also try home remedies and lifestyle changes.
3 Does vitamin C help with hyperpigmentation?
Yes, vitamin C can help with hyperpigmentation. It can reduce the appearance of dark spots and hyperpigmentation caused by aging, sun exposure, and inflammation.
4 Which serum is best for pigmentation?
Serums that contain alpha arbutin, niacinamide, or vitamin C can help with pigmentation. When choosing a serum, you can also consider your skin type.
5 What is the best treatment for skin pigmentation?
Treatments for skin pigmentation include chemical peels, laser therapy, topical treatments, and prescription medications.




